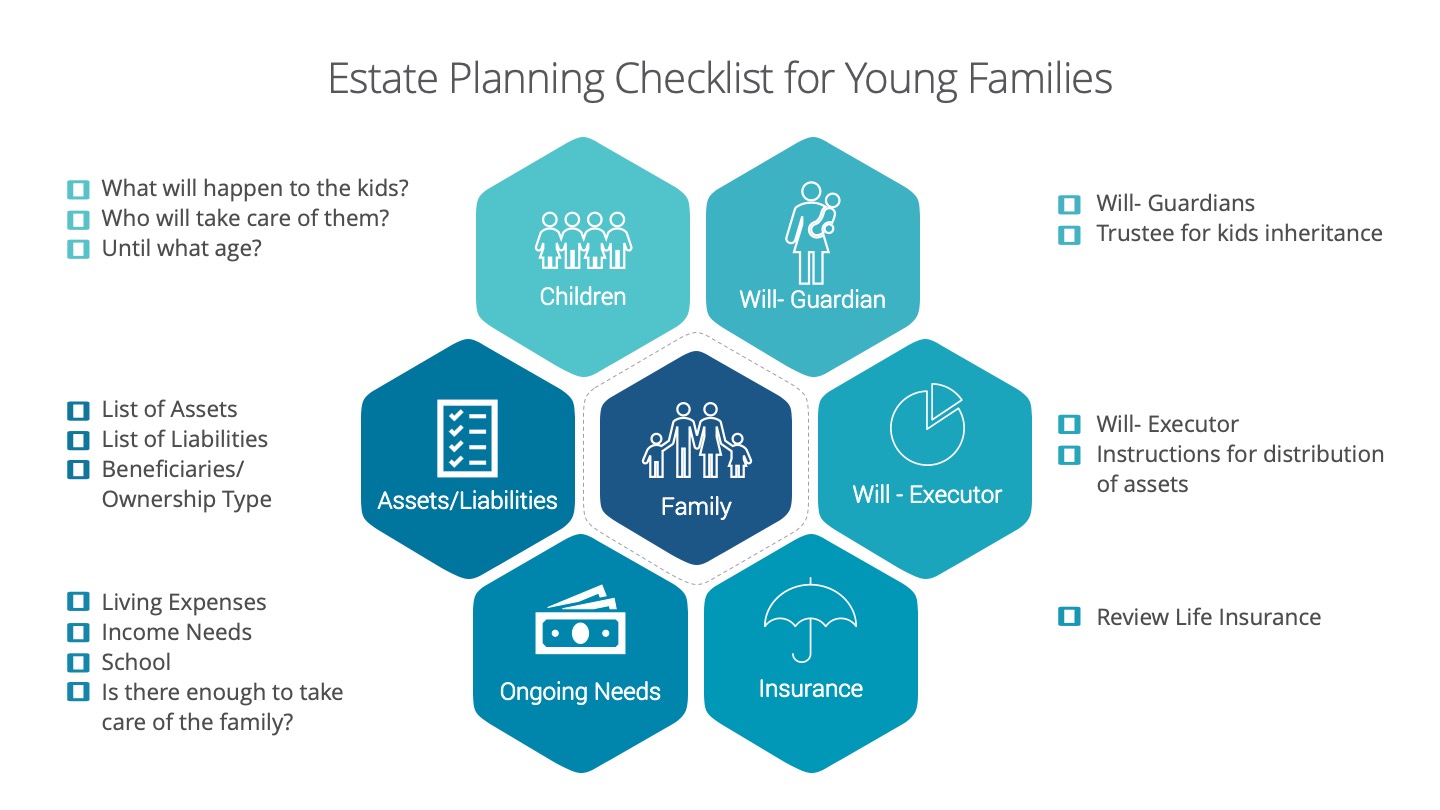
Estate Planning for Young Families
Having a family is a blessing and can also bring a lot of worry. A lot of this worry can stem from not being prepared for a disaster like if something were to happen to you or your spouse.
We’ve put together an infographic checklist that can help you get started on this. We know this can be a difficult conversation so we’re here to help and provide guidance.
The Children
-
What will happen to the children if both parents were to pass away?
-
Who would take care of them and until what age?
-
What would happen if only parent were to pass away?
Make sure you have a will that:
-
Assigns a guardian for your children
-
If there’s an inheritance for the children, who will take care of this? Make sure you assign a trustee for the inheritance.
-
Always choose 2 qualified people for each position and communicate your intentions with them to ensure they’re up for the responsibility.
Assets and Liabilities
-
What are your assets? Create a detailed list of your assets such as: Home, Family Business Interest, Investments- Non registered, TFSA, RRSP, RDSP, RESP, Company Pension Plan, Insurance Policy, Property, Additional revenue sources, etc…
-
What are your liabilities? Create a detailed list of your liabilities such as: Mortgage, Loans (personal, student, car), Line of Credit, Credit card, Other loans (payday, store credit card, utility etc.)
-
Understand your assets-the ownership type (joint, tenants in common, sole etc.), list who are the beneficiaries are for your assets
-
Understand your liabilities- who’s on the hook for paying back the loan?
Make sure you have a will that:
-
Assigns an executor
-
Provide specific instructions for distribution of assets
-
Always choose 2 qualified people for each position and communicate your intentions with them to ensure they’re up for the responsibility.
Ongoing Needs
What are your family’s ongoing needs?
-
List out the living expenses
-
List out income needs
-
Do you still need to pay for school?
-
Determine if you have enough (assets minus liabilities) to take care of the family.
Make sure you review your insurance.
-
Once you determine how much need there is, review your life insurance coverage to see if it meets your needs or if there’s a shortfall.
Execution: It’s good to go through this but you need to do this. Besides doing it yourself, here’s a list of the individuals that can help:
-
Financial Planner/Advisor (CFP)
-
Estate Planning Specialist
-
Insurance Specialist
-
Lawyer
-
Accountant/Tax Specialist
-
Chartered Life Underwriter (CLU)
-
Certified Executor Advisor (CEA)
There are definitely unique situations in many families and things can get complicated so please use this when you feel it’s applicable.
Next steps…
-
Contact us about helping you get your estate planning in order so you can gain peace of mind that your family is taken care of.