The end of 2023 is quickly approaching – which means it’s time to get your paperwork in order so you’re ready when it comes time to file your taxes!
In this article, we’ve covered five different major types of 2023 personal tax tips:
Investment Considerations
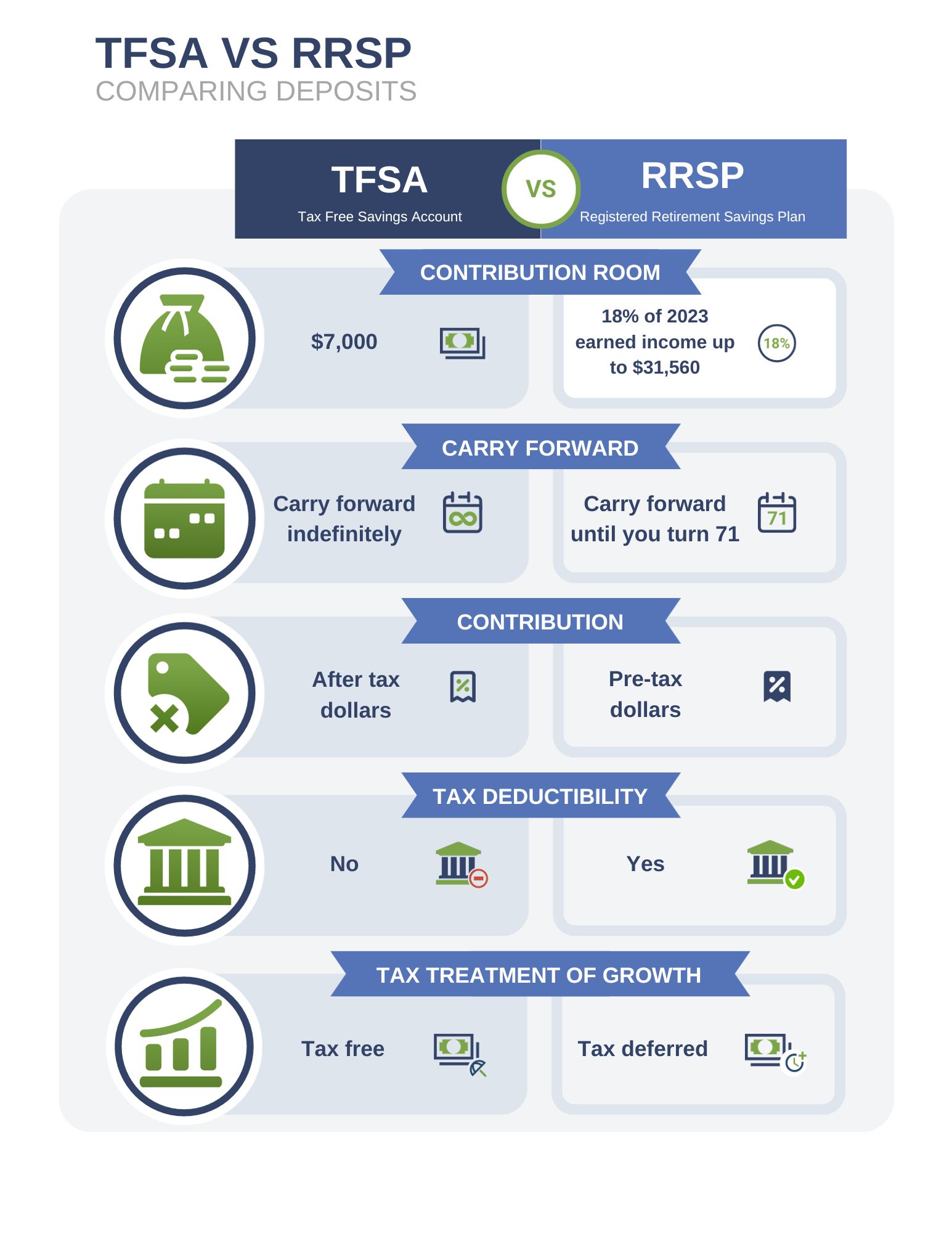
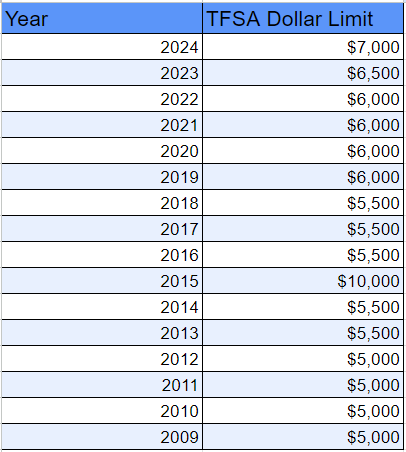
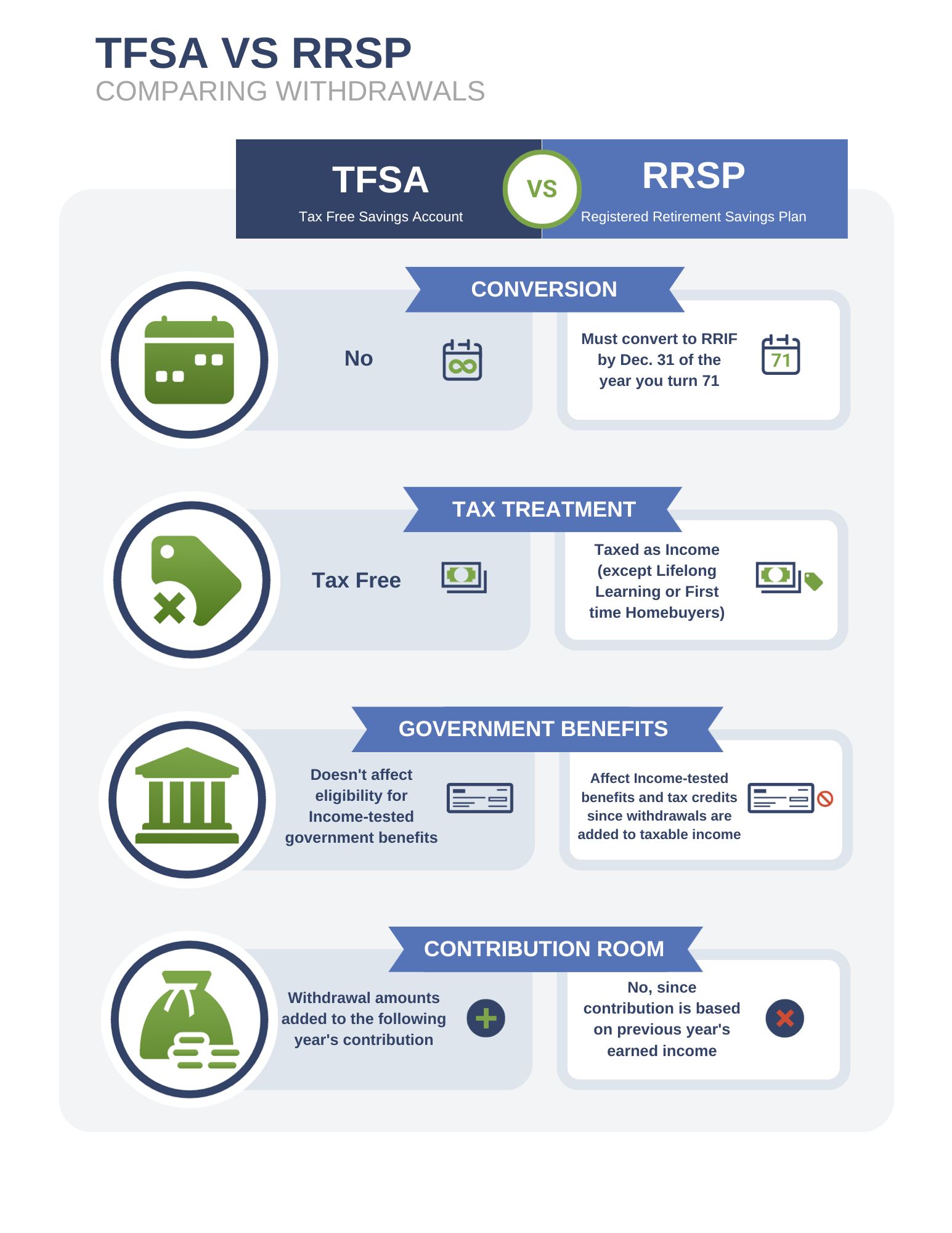
Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA)-You can contribute up to a maximum of $6,500 for 2023. You can carry forward unused contribution room indefinitely. The maximum amount you’re allowed to make in TFSA contributions is $88,000 (including 2023) if you have been at least 18 years old and resident in Canada since 2009.
Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP) – For the 2023 tax year, you have until February 29, 2024, to contribute to your Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP) or a spousal RRSP. However, contributing earlier can benefit you more due to tax-deferred growth. Your deduction limit for 2023 is 18% of your 2022 income, up to $30,780, but this will reduce if you have pension adjustments. Don’t forget, any unused contribution room from previous years or pension adjustment reversals can increase your limit.
Also, you can deduct contributions on your 2023 income if they are made within the first 60 days of 2024. It’s possible to defer these deductions to a later year if that suits your financial strategy better. To optimize your RRSP, consider holding investments that have the potential for growth outside of your RRSP to take advantage of lower taxes on capital gains and dividends. Within your RRSP, keep investments that generate regular interest income. If you’re unsure about the best investment strategy for your RRSP, our team is ready to provide expert advice to help you maximize your retirement savings.
Do you expect to have any capital losses? If you have capital losses, sell securities with accrued losses before year end to offset capital gains realized in the current or previous three years. You must first deduct them against your capital gains in the current year. You can carry back any excess capital losses for up to three years or forward indefinitely.
Interest Deductibility – If possible, repay the debt that has non-deductible interest before other debt (or debt that has interest qualifying for a non-refundable credit, i.e. interest on student loans). Borrow for investment or business purposes and use cash for personal purchases. You can still deduct interest on investment loans if you sell an investment at a loss and reinvest the proceeds from the sale in a new investment.
Tax Loss Selling- Tax-loss selling is when you sell investments that have lost value by the end of the year from accounts that are not tax-deferred. This helps to offset any profits you made from other investments. If your losses are greater than your profits, you can use these extra losses to reduce taxes on profits from the last three years or save them to lower taxes on future profits.
For your losses in 2023 (or the past three years) to count, you need to complete the sale by December 27, 2023. This is because it needs to be settled by the end of the year, and December 30th and 31st are on a weekend in 2023.
If you sell an investment at a loss and plan to buy it again soon, you should know about the “superficial loss” rule. This rule applies if you sell something for a loss and buy it back within 30 days before or after selling it. It also applies if someone close to you, like your spouse or partner, a company they or you control, or a trust where you or they are the main beneficiaries (like your RRSP or TFSA), buys it within 30 days and still has it after 30 days. If this happens, you can’t use that loss to reduce your taxes right away. Instead, the loss gets added to the cost of the investment you bought back. You’ll only get the tax benefit from this loss when you sell this investment later.
When it comes to transferring investments, you might think about moving one with a loss into your RRSP or TFSA to count the loss without really selling it. But the tax rules don’t allow this, and there are big penalties for swapping an investment from a regular account to a registered account like an RRSP or TFSA.
To avoid these issues, it’s better to sell the investment that’s lost value and, if you have room, put the money from the sale into your RRSP or TFSA. Then, if you want, your RRSP or TFSA can buy the investment again after waiting for 30 days since the initial sale. This way, you avoid the superficial loss rule.
Individuals
The following list may seem like a lot, but it’s unlikely every single tip will apply to you. It’s essential to make sure you aren’t paying taxes unnecessarily.
COVID-19 federal benefits – If you return any amounts you received from COVID-19 benefits before the year 2023, you have the option to deduct the amount you paid back from your income for the year when you originally received the benefit, rather than the year in which you repay it.
Income Timing – If your marginal personal tax rate is lower in 2024 than in 2023, defer the receipt of certain employment income; if your marginal personal tax rate is higher in 2024 than in 2023, accelerate.
Medical expenses – If you have eligible medical expenses that weren’t paid for by either a provincial or private plan, you can claim them on your tax return. You can even deduct premiums you pay for private coverage. Either spouse can claim qualified medical expenses for themselves and their dependent children in a 12-month period, but it’s generally better for the spouse with the lower income to do so.
Charitable donations – Tax credits for donations are two-tiered, with a more considerable credit available for donations over $200. You and your spouse can pool your donation receipts and carry donations forward donations for up to five years. If you donate items like stocks or mutual funds directly to a charity, you will be eligible for a tax receipt for the fair market value, and the capital gains tax does not apply.
Moving expenses – If you’ve moved to be closer to school or a place of work, you may be able to deduct moving expenses against eligible income. You must have moved a minimum of 40 km.
Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT)- The AMT framework is a taxation system that sets a minimum amount of tax for individuals who utilize specific tax deductions, exemptions, or credits to substantially reduce their tax liabilities to exceedingly low levels. With AMT, there’s a parallel tax calculation that doesn’t allow as many deductions, exemptions, or credits as the regular way of calculating taxes. If the tax amount computed under the AMT system exceeds the tax liability determined under the regular tax system, the surplus amount becomes payable as AMT for the year.
Recent government proposals have outlined forthcoming adjustments to the AMT system, set to take effect in 2024. These proposed modifications encompass elevating the AMT tax rate, enhancing the AMT exemption threshold, and expanding the AMT tax base by constraining specific exemptions, deductions, and credits that serve to reduce overall tax obligations.
For individuals whose taxable income surpasses approximately $173,000, and who derive income subject to lower tax rates than standard income, or those who benefit from deductions or credits that mitigate their tax liabilities (such as capital gains, stock options, Canadian dividends, unused non-capital losses from preceding years, or non-refundable tax credits like the donation tax credit), it is anticipated that their AMT liabilities in 2024 may exceed those incurred in 2023.
To navigate these impending changes effectively and make financial decisions, it is advisable for individuals to seek counsel from a tax professional.
Families
Childcare Expenses – If you paid someone to take care of your child so you or your spouse could attend school or work, then you can deduct those expenses. A variety of childcare options qualify for this deduction, including boarding school, camp, daycare, and even paying a relative over 18 for babysitting. Be sure to get all your receipts and have the spouse with the lower net income claim the childcare expenses. In addition, some provinces offer additional childcare tax credits on top of the federal ones.
Caregiver – If you are a caregiver, claim the available federal and provincial/territorial tax credits.
Children’s fitness, arts and wellness tax credits – If your child is enrolled in an eligible fitness or arts program, you may claim a provincial or territorial tax credit for fitness and arts programs.
Estate planning arrangements
-
Periodic Review: It is imperative to conduct an annual review of your estate planning arrangements to verify that they are in alignment with your objectives and compliant with current tax regulations.
-
Probate Fee Mitigation: Deliberate strategies should be explored to minimize probate fees.
-
Will Examination: Regularly reviewing your will is crucial to ensure it remains valid and aligns with your evolving life and estate planning requirements.
Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP) – can be a great way to save for a child’s future education. The Canadian Education Savings Grant (CESG) is only available on the first $2,500 of contributions you make each year per child (to a maximum of $500, with a lifetime maximum of $7,200.) If you have any unused CESG amounts for the current year, you can carry them forward. If the recipient of the RESP is now 16 or 17, they can only receive the CESG if a) at least $2,000 has already been contributed to the RESP and b) a minimum contribution of $100 was made to the RESP in any of the four previous years.
Registered Disability Savings Plan (RDSP) – If you have an RDSP open for yourself or an eligible family member, you may be able to get both the Canada Disability Savings Grant (CDSG) and the Canada Disability Savings Bond (CDSB) paid into the RDSP. The CDSB is based on the beneficiary’s adjusted family net income and does not require any contributions to be made. The CDSG is based on both the beneficiary’s family net income and contribution amounts. In addition, up to 10 years of unused grants and bond entitlements can be carried forward.
First Home Savings Account (FHSA) – If you are a Canadian resident, age 18 or older and planning to become first-time homebuyers. Starting from April 1, 2023, this account serves as a valuable tool for saving towards the purchase of a qualifying first home.
The FHSA program comes with an annual contribution limit of $8,000, and a cumulative lifetime cap of $40,000, with the flexibility to carry forward up to $8,000 in unused contributions. Importantly, contributions made to the FHSA are tax-deductible, offering potential tax benefits. Additionally, the returns earned on your savings within this account are not subject to taxation, which can enhance the overall growth of your savings. Most notably, when you make qualifying withdrawals to buy your first home, these withdrawals are non-taxable.
Retirees
Registered Retirement Income Fund (RRIF) – Turning 71 this year? If so, you are required to end your RRSP by December 31. You have several choices on what to do with your RRSP, including transferring your RRSP to a registered retirement income fund (RRIF), cashing out your RSSP, or purchasing an annuity. Talk to us about the tax implications of each of these choices.
Pension Income- Are you 65 or older and receiving pension income? If your pension income is eligible, you can deduct a federal tax credit equal to 15% on the first $2,000 of pension income received – plus any provincial tax credits. Don’t currently have any pension income? You may want to think about withdrawing $2,000 from an RRIF each year or using RRSP funds to purchase an annuity that pays at least $2,000 per year.
Canada Pension Plan (CPP) – If you’ve reached the age of 60, you may be considering applying for CPP. Keep in mind that if you do this, the monthly amount you’ll receive will be smaller. Also, you don’t have to have retired to be able to apply for CPP. Talk to us; we can help you figure out what makes the most sense.
Old Age Security – For individuals aged 65 or older, securing enrollment in Old Age Security (OAS) benefits is essential. It’s important to note that retroactive OAS payments are limited to a maximum of 11 months plus the month in which you apply for your OAS benefits. Moreover, if you encounter OAS clawback challenges due to exceeding income thresholds, there are strategic measures you can take including income splitting or reduction.
If eligible, you can opt to defer the initiation of your OAS benefits for up to 60 months after turning 65. This choice results in a permanent increase of 0.6% in your monthly OAS payment for each month of deferral.
These financial strategies, when combined with timely enrollment in OAS benefits, can help you navigate OAS-related matters effectively, ensuring you receive the maximum benefits available to you while optimizing your retirement income.
Estate planning arrangements – Review your estate plan annually to ensure that it reflects the current tax rules. Consider strategies for minimizing probate fees. If you’re over 64 and living in a high probate province, consider setting up an inter vivos trust as part of your estate plan.
Students
Education, tuition, and textbook tax credits – If you’re attending post-secondary school, claim these credits where available.
Canada tuition credit – If you’re between 25 to 65 and enrolled in an eligible educational institution, you can claim a federal tax credit of $250 per year, $5,000 maximum lifetime tax credit. You can claim tuition paid on your taxes, carry the amount forward, or transfer an unused tuition amount to a spouse, parent, or grandparent.
Need some additional guidance?
Reach out to us if you have any questions. We’re here to help.